The research titled “The Importance of Digital Literacy in Promoting Sustainable Development: A Case Study of Buea Community” explores the critical role of IT skills in enhancing youth employability and fostering sustainable development. The study focuses on Buea, a city in the South West Region of Cameroon, which has been significantly impacted by the Anglophone crisis. This crisis has disrupted the education system, leaving many youths without access to essential digital education, which has, in turn, affected their likelihood of getting a job and hindered sustainable development in the region.

Buea is known for its vibrant youth population and is supported by multiple universities, making it a hub of academic activity and youthful energy. According to the Human Rights Watch in 2020, the crisis has caused many youths estimated to be more than 855,000 to leave school, thus missing out on crucial digital education. The city’s diverse economic landscape, comprising established businesses and start-ups, makes it an ideal location to understand the dynamics of youth employment and the importance of IT skills, especially in the context of the educational disruption caused by the crisis.
The survey conducted in Buea targeted both employers and employees to gain insights into the current job market and the critical importance of IT skills. Among the employee respondents, 55% were aged between 23-30, 31% were aged 17-22, and the gender distribution was nearly balanced, with 53% male and 47% female respondents. The educational qualifications varied, with 34% holding a Bachelor’s degree and 10% possessing a Master’s degree. These demographics highlight the diversity of the youth population that has been adversely affected by the crisis, impacting their educational journey and access to digital literacy.
Insights from Employers on how they Perceive The Importance of Digital Literacy in Promoting Sustainable Development
Employers’ responses validated the critical role of IT skills. Among the employers surveyed, 65% considered IT skills as very important for the positions they were hiring for, and 74.6% assessed IT skills during the hiring process. The diversity of industries represented by the employers, ranging from IT and technology to agriculture and entertainment, underscores the universal demand for IT skills across various sectors.
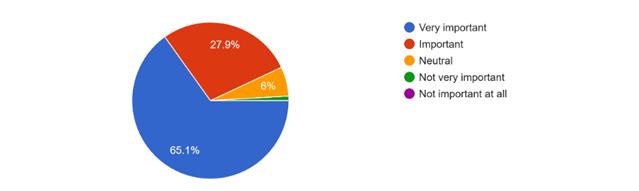
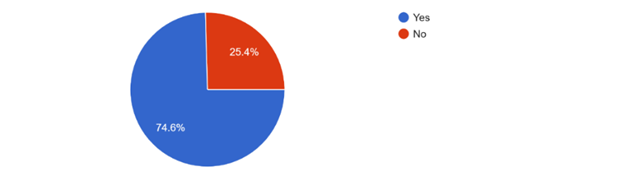
Insights from Employees
Key findings from the employee survey included an overwhelming interest in IT training, with 81% of respondents expressing a desire to acquire digital skills, and 87% willing to participate in free IT training programs. This interest underscores the urgent need for initiatives like EYODS to provide accessible digital education and training opportunities, especially for youths who have been left behind due to the crisis. Furthermore, 53% of employees strongly agreed and 39% agreed that IT skills improve their job chances, underscoring the perceived value of digital literacy in securing employment and advancing careers.
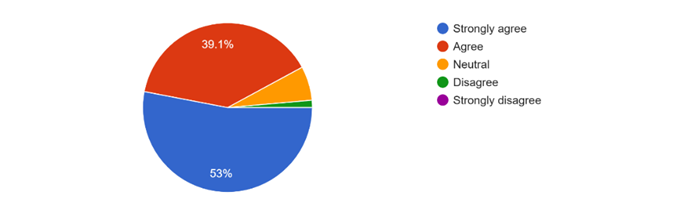
Employers’ feedback also highlighted the real-world implications of lacking IT skills, with 58% of employers reporting rejections due to insufficient digital proficiency. This situation is worsen in regions like Buea, where the crisis has severely limited youths’ opportunities to gain these essential skills.
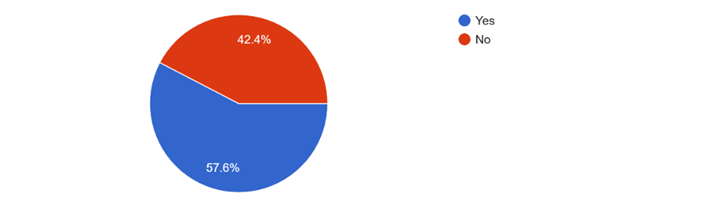
The research highlights the specific types of IT training that young individuals are interested in, such as programming, digital marketing, basic computer skills, web development, graphic designing, and cyber security. This variety reflects the diverse career aspirations of the youth and emphasizes the importance of offering a wide range of IT training programs to cater to different interests and needs. Practical tasks, certifications, and tests are commonly used by employers to assess IT skills during the hiring process, indicating that both practical experience and formal qualifications are essential for demonstrating digital proficiency. In a crisis-affected area like Buea, providing such diverse training programs is crucial to help bridge the skills gap.

In conclusion, the research demonstrates the mandatory role of digital literacy in promoting sustainable development and reducing unemployment among youths, especially in crisis-affected regions like Buea. The findings from both employers and employees underscore the critical importance of IT skills in today’s job market. By expanding access to IT training, promoting continuous learning, and collaborating with employers, we can bridge the skills gap and provide young individuals with the tools they need to succeed.
Initiatives like EYODS (Education Youths on Digital Sustainability With Emphasis on the Girl Child) are essential in this effort, helping to equip the youth with the digital literacy necessary to thrive in a rapidly evolving technological world and contribute to sustainable development in regions impacted by educational disruptions.
Learn more about GoGreen Technologies
Contact us Here
Or you can Join forces with us
